Today, the design industry is continuously evolving, thanks to the help of modern technology. Computer-aided design (CAD) software allows design professionals in industries such as architecture and construction, industrial and product design, computer animation, and more to create, collaborate, and share innovative ideas with ease.
Computer-aided design software has indeed come a long way in boosting the productivity and efficiency of design professionals. That said, here are some things you need to know about CAD software and why it has become integral to the design industry today.
The Origins Of Computer-Aided Design
The concept of computer-aided design was initially developed in the 1960s by Patrick Hanratty and Ivan Sutherland. While it is known that Pierre Ettiene Bezier, a French engineer, is one of the founders of solid, geometric, and physical modeling, Hanratty was believed to have created the first numerically controlled program that allowed designers to draw simple lines with a computer in 1950, making him known as the Father of CAD.
Numerical control systems and interactive graphics were combined and after two years Sutherland began working on a design to revolutionize 3D computer modeling and visualization. This system allowed designers to draw engineering diagrams on a cathode-ray tube (CRT) display using a light pen.
Later in 1972, Hanratty founded a company and began developing an “Automated Drafting and Machining” (ADAM) program. Many of the commands present in this program are still used in modern CAD design software programs. It ran on a 16-bit computer.
Users could use a keyboard instead of numerical controls to operate a small drawing command table. Many CAD systems today are based on this program making them very efficient tools when it comes to designing.
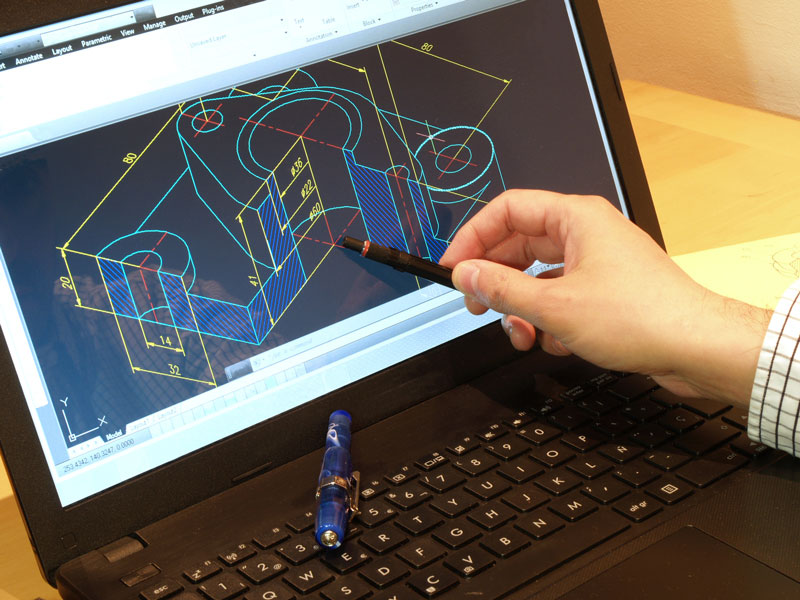

The Purpose Of Computer-Aided Design
Technology has definitely revolutionized the design industry by optimizing the overall design process thru the use of computer-aided design software. This technological advancement has replaced the practice of drafting plans manually and is now allowing designers and their clients to visualize a project’s concept and details either in 2D drawings or 3D models.
CAD software enables design professionals to produce precise drawings and modify them more efficiently to boost productivity. For instance, an architect can finalize the space planning of a house project thru a 2D floor plan. Some CAD software even allows designers to merge and overlay plans of different engineering trades, such as electrical, plumbing, and mechanical. This can result in a more efficient plan and improved coordination among design professionals, helping avoid possible construction clashes and issues. And if there are modifications needed, revisions can be done in no time. And since any form of revision is critical to the production or construction process, CAD software can aid in determining these changes, highlighting how these details affect the entire design model.
The Applications Of Computer-Aided Design Software
CAD software was developed to help simplify and optimize the overall design process. With that said, design professionals use CAD to be more efficient in the production of drawings and outputs such as:
-
Floor Plans and Drawings
Floor plans are drawings that show the actual layout of the house or room to be constructed. These drawings typically reflect the relationship of each space, traffic flow of the users, furniture layout, lighting layout, plumbing layout, and more.
-
Technical Drawings and Diagrams
A technical diagram is simply a drawing that reflects all technical details such as connection details, material specification, and more, that are essential for the construction process.
For instance, an instrumentation and piping diagram (PID) shows the relationship between a flow’s instrumentation and piping components. A P&ID shows the different types of valves, pumps, tanks, and other elements within a more extensive system and how they are connected.
-
Three-Dimensional Model and Renderings
Aside from generating technical plans and details, CAD software also allows designers to build a realistic model to help simulate the proposed design elements thru a 3D model and renderings.
Visions and ideas are easily translated into the design, which can then be converted into drawings later on. Much like a physical scale model, a three-dimensional model allows designers to play around and explore creative ideas best for the project. And since it is running on a digital platform, revisions and schemes can be easily done.
From these 3D models, designers can then create photo-realistic rendered images, which can significantly help them and their clients to visualize the project.
Conclusion
The design industry is complex as it is. Sorting out and finalizing technical details requires careful analysis and consideration. A computer-aided design program can be beneficial in this regard.
Computer-aided software does not simply help optimize the design process but also allows designers to interact with their designs and creations either in 2D format or 3D models. With this kind of advancement, projects are expected to run smoothly. There’ll be more accurate and comprehensive plans to follow, which can not only speed up the production or construction process but also help manage costs in the long run.